Domain Name Service (DNS) was designed to translate a domain name (www.youtube[dot]com) into an IP address (208.65.153.238) that the Internet can understand and route.
It uses TCP/UDP Port 53.
DNS can use both transmission protocols TCP and UDP. But UDP is preferred protocol because of its simplicity and speed.
TLD & Subdomains
Domain names are registered with ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) usually through an intermediary such as GoDaddy.
TLD's (Top Level Domains) include .com, .edu, .org and many others seen at the end of Full Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
DNS works in a hierarchical manner.
TLD's can have multiple sub domains under them.
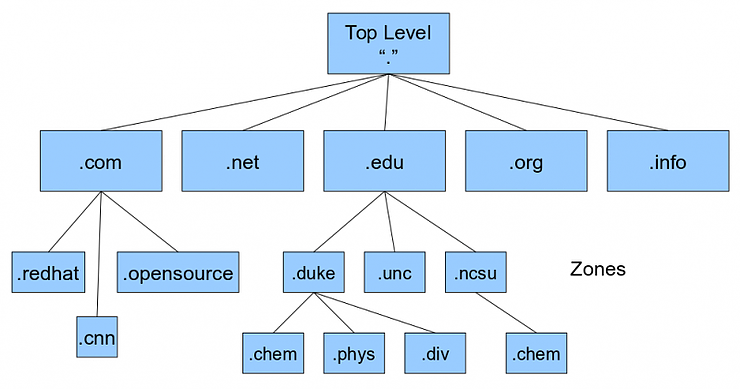
A sub domain is a domain that is part of larger domain. Example, Above .cnn or .redhat are Second level Domain (SLD) or sub domain under .com or domain name.
Beneath SLD's there can be many domains like sales.redhat[.]com etc.
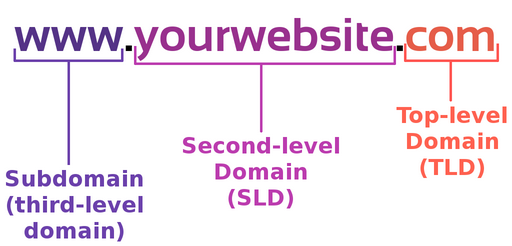
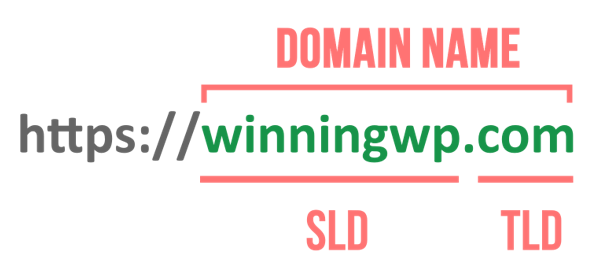
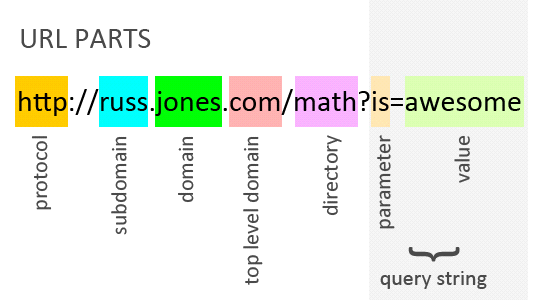
URL(Uniform Resource Locator)
URL is the address of a specific webpage or file on the Internet.
For example, the URL of the TechTerms website is "http://techterms.com."
The URL bar or the Address bar of a web browser contains the address(URL) of a website.
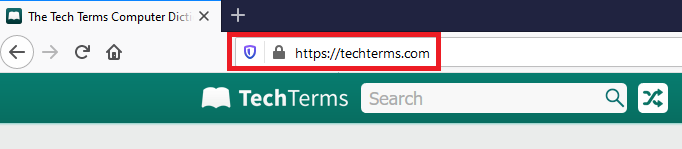
It includes the following elements:
- URL prefix (http://) - specifies the protocol used to access the location
- Domain name (techterms.com) – the server/host name or IP address of the server
- /definition/url – the path to the directory or file
Various URL prefixes:
- http – for a webpage, website directory, or other file available over HTTP
- mailto – for an email address (often used to redirect browsers to an email client)
- ftp – for a file or directory of files available to download from an FTP server
- file - for a file located on a local storage device (technically not a URL because it does not refer to an Internet-based location)
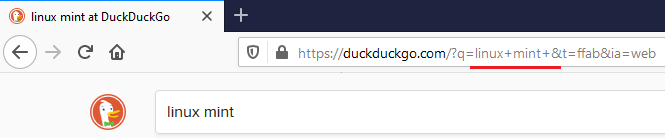
NOTE: URL uses forward slashes to denote different directories and cannot contain spaces. Therefore, ‘+’ or ‘%20’ signs , dashes ‘-‘ and underscores ‘_’ are often used to separate words within a web search and address.
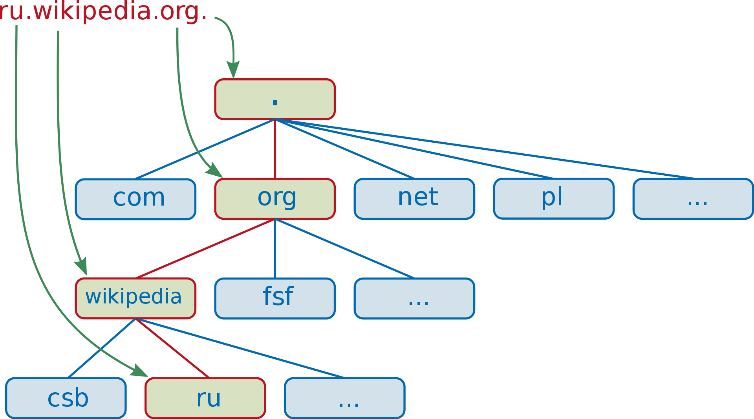
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or Absolute domain
It is the complete domain name of a specific computer or host online.
Format:
[hostname].[domain].[tld].
Hostname - identifies a hardware device or host on a network. It is used in both on LAN and the Internet.
Example: "www.techterms.com[.]" is an FQDN since it contains
- a hostname ("www") and
- a domain name ("techterms.com"), followed by a trailing period (.)
FQDN has four parts:
-
Hostname: www, mail, ftp, store, support, etc.
It often specifies a particular service or protocol -
Domain: instagram, google, facebook, etc.
Domain might also include subdomains. -
Top level domain (TLD): .com, .net, .org, .co.uk, etc.
-
Trailing period: an empty element (period ‘.’) to the right of the TLD that signifies the unnamed domain root zone (Internet).
A trailing period ‘.’ follows the TLD - www.GoDaddy[.com.]
These days Internet browser and other software usually processes the trailing period for us.
Root Servers
FQDN specifies its location from the absolute root of the DNS system (root servers).
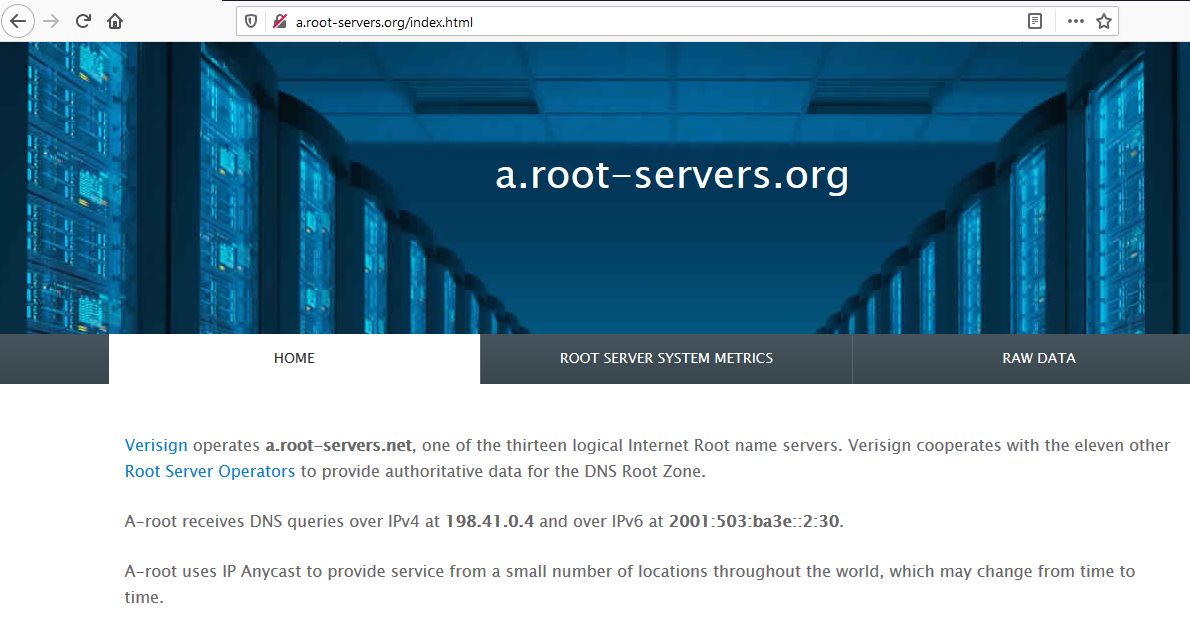
Root severs or DNS root name servers publish root zone file contents which provides DNS functionality to the Internet.
root zone file is at the top of DNS databases.
It contains numeric IP addresses of the authoritative DNS servers for all top-level domains (TLDs) like com, org, edu, and the country code top-level domains.
Internet traffic never passes through root servers. Instead, root servers answer queries from sections of the DNS.
A number of root servers are located around the world.
Partially Qualified Domain Names(PQDN) - URL which do not include “www” (hostnames).
Why use WWW in domain?
We use www in a domain because of performance, technical and security issues.
- Cookies are passed down to subdomains
Cookies set from a hostname, will also be sent to all subdomains. i.e. if the website on “example.com” sets a cookie, the browser will also send this cookie to www.example.com, cdn.example.com and other thirdpartyservice.example.com while visiting them.
These cookies can be read and shared by third parties. This in turn creates security and performance issues.
A cookie set from “www.example.com” will not be sent to any “sibling” hosts as browser understands that they are not “subservices” but completely different services.
- No Scalability
When a site grows large and you move it to a hosted service, point it to a WAF(Web Application Firewall) or a DDoS mitigator you will use a CNAME type record, to point the hostname to another flexible hostname that is managed by a vendor (like Cloudflare) but without ‘www’ it will not be possible.